Calculating CO2
With ClimatePartner as a long-term partner for the implementation of our climate targets, the corporate carbon footprint (CCF) is calculated using various key figures.
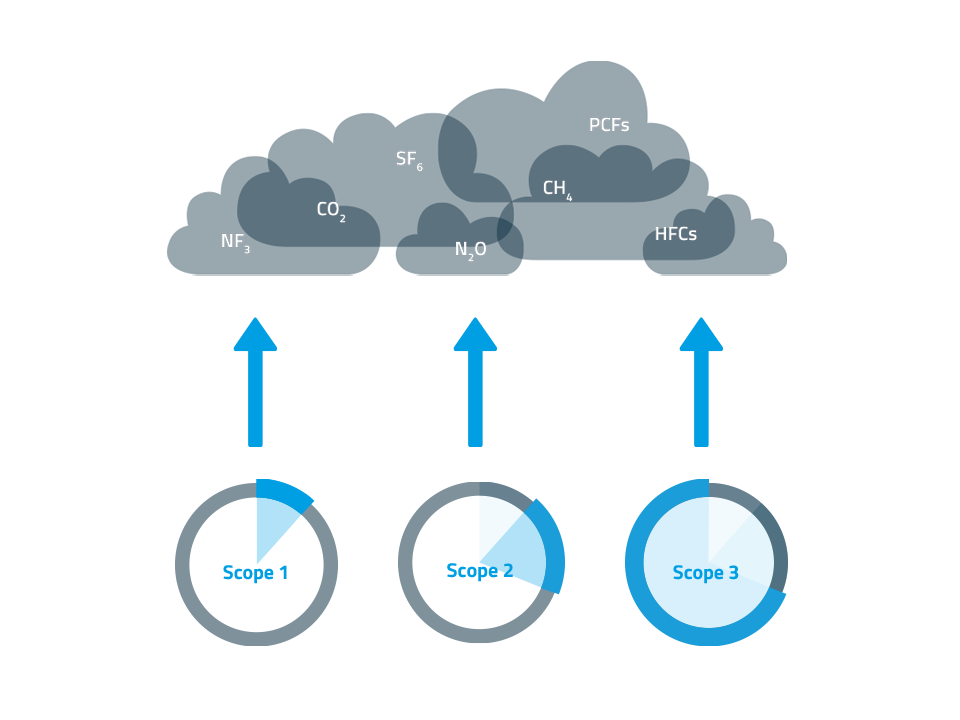
In accordance with the Greenhouse Gas Protocol (GHG Protocol), the carbon footprint is divided into so-called “scopes”, sub-areas of emissions. These include emissions from the vehicle fleet, electricity consumption and indirect emissions from the value chain.

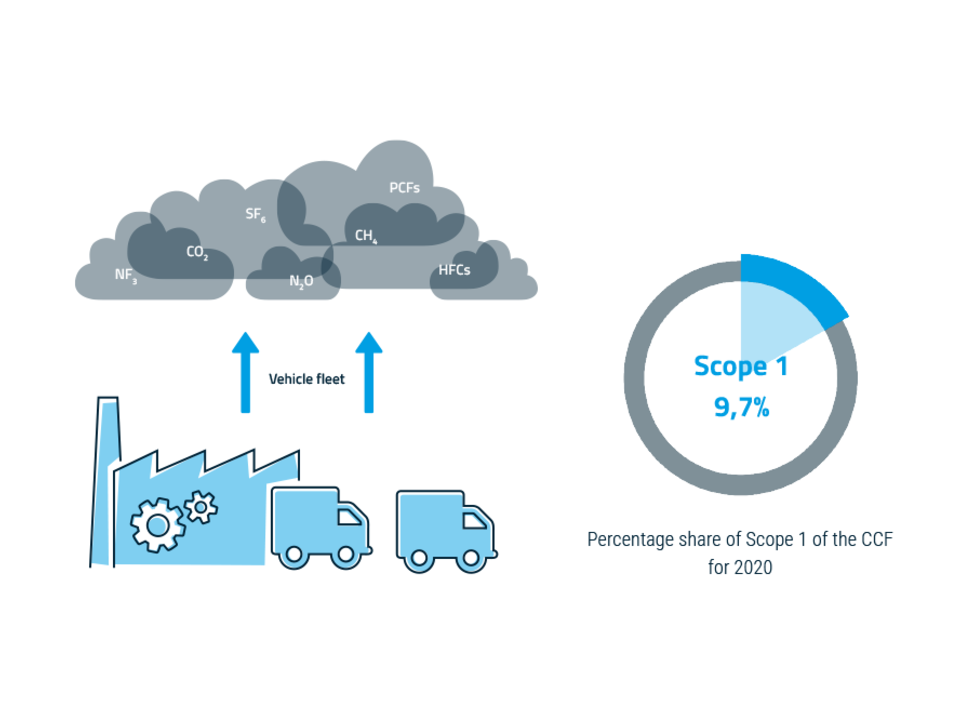
Scope 1 - direct emissions
Scope 1 emissions are directly attributable to or controlled by the company. This includes emissions from energy sources at the company site, such as natural gas and fuels, coolants, as well as emissions from the operation of boilers and ovens. Scope 1 also includes emissions from the company's own vehicle fleet (e.g. cars, delivery vans, trucks, helicopters for hospitals, etc.).

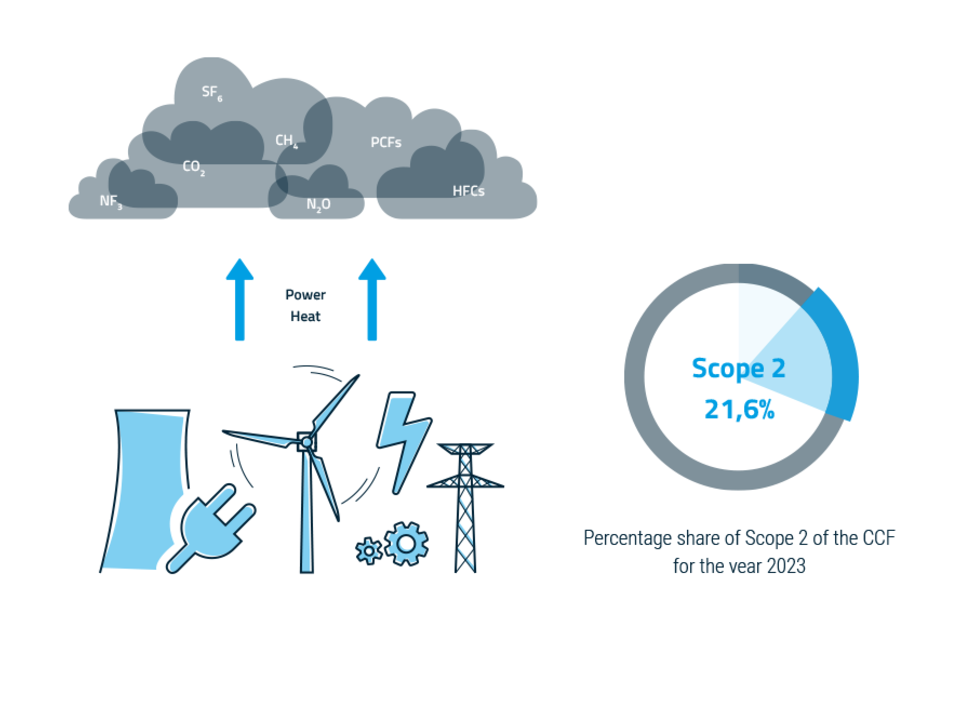
Scope 2 - indirect emissions
Scope 2 emissions are indirect greenhouse gas emissions from purchased energy, such as electricity, steam, district heating or cooling, which are generated outside the company's own system boundaries but consumed by the company. For example, electricity purchased by a utility company is generated outside the company, so the resulting emissions are considered indirect emissions.

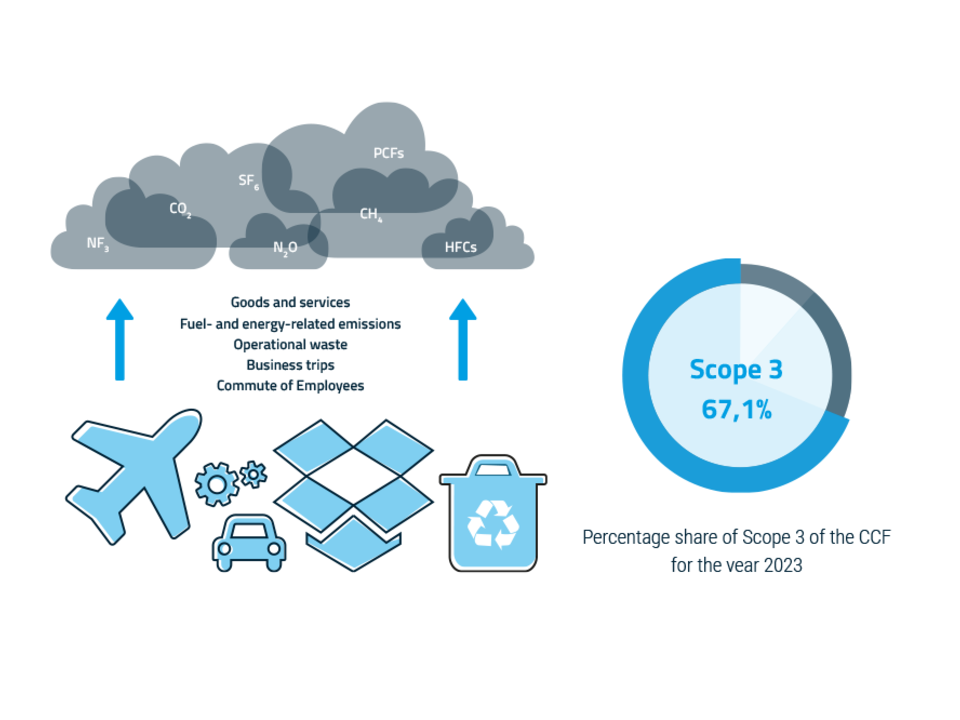
Scope 3 - indirect emissions from the value chain
Scope 3 includes all indirect emissions that occur along the value chain. To make a clear distinction between Scope 2 and Scope 3, the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) describes Scope 3 emissions as “the result of activities from facilities that are not owned or controlled by the company, but the company directly influences these activities within its own value chain.”